The proximate composition and physical analysis of flatbreads prepared from millet flour, sunflower cake, and beets with added fresh garlic, jalapeno pepper, and red onion and their relationship to nutrition and health benefits
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Kahlon Talwinder, Avena-Bustillos Roberto, Friedman Mendel, Haff Ronald
Research Articles | Published: 11 March, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 958
Keywords: Millet, Beets, Garlic, Jalapeno pepper, Onions
Abstract
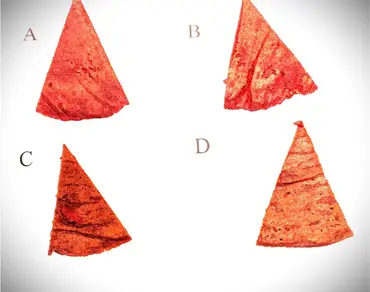
The objective of the present study was to determine the proximate composition (protein, crude fat, minerals, carbohydrate, and water) and physical properties (water activity, true and bulk densities, and texture) of flatbreads prepared from gluten-free high-protein ingredients supplemented with fresh garlic, jalapeno pepper, and red onion. The aim was to create nutritious gluten-free, vegetable flatbreads with ≥ 30% protein content (dry-weight basis). We prepared and analyzed the following four flatbread categories: Millet-Sunflower Cake-Beets (MScB), MScB-Garlic, MScB-Jalapeno Pepper, and MScB-Red Onion. The protein content of evaluated flatbreads on a dry weight basis was 32–36%, which exceeded our objective by 2–6%. The flatbread tested contained only 0.5% added salt and 3.8–4.1% total essential minerals. The novel flatbreads, prepared by baking the dough for 2 min (1 min on each side at 165–195 °C), require only three to four ingredients and can be made in any household kitchen or by commercial production. These flatbreads offer nutritious, gluten-free foods suitable for gluten-sensitive individuals. In addition, the collated information of published studies on the nutritional and health benefits of the individual ingredients used to prepare the flatbreads (millet, sunflower cake, beetroots, garlic, peppers, and onions) will hopefully facilitate and guide further research to help improve human nutrition and health.
References
AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 14th ed.; Association of Analytical Chemists: Washington DC, USA, 1984; Method 27.006.
AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemist: Washington DC, USA, 1990; Methods 923.03 and 935.29.
AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 17th ed.; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000; Method 990.03.
Babateen AM, Shannon OM, O’Brien GM, Olgacer D, Koehl C, Fostier W, Mathers JC, Siervo M (2023) Moderate doses of dietary nitrate elicit greater effects on blood pressure and endothelial function than a high dose: a 13-week pilot study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 33:1263–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2023.02.024
Bangar PS, Singh A, Chaudhary V, Sharma N, Lorenzo JM (2023) Beetroot as a novel ingredient for its versatile food applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 63:8403–8427. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2055529
Blicharz-Kania A, Pecyna A, Zdybel B, Andrejko D, Marczuk A (2023) Sunflower seed cake as a source of nutrients in gluten-free bread. Sci Rep 13:10864. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38094-w
Catalfamo LM, Marrone G, Basilicata M, Vivarini I, Paolino V, Della-Morte D, De Ponte FS, Di Daniele F, Quattrone D, De Rinaldis D et al (2022) The utility of Capsicum Annuum L. in internal medicine and in dentistry: a comprehensive review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:11187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811187
McGee, H. On Food and Cooking: The Science and Lore of the Kitchen; Simon & Schuster, 2003; ISBN 978–0–684–84328–5.
Chung M-Y, Hwang J-T, Park S-H (2023) Antiobesity effects of onion (Allium Cepa) in subjects with obesity: systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Sci Nutr 11:4409–4418. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.3426
Crawford LM, Kahlon TS, Chiu M-CM, Wang SC, Friedman M (2019a) Acrylamide content of experimental and commercial flatbreads. J Food Sci 84:659–666. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14456
Crawford LM, Kahlon TS, Wang SC (2019b) Mendel friedman acrylamide content of experimental flatbreads prepared from potato, quinoa, and wheat flours with added fruit and vegetable peels and mushroom powders. Foods 8:228
FDA 2024. Gluten and food labeling
Flatbread varieties from around the world available online: https://www.thespruceeats.com/flatbread-varieties-1328776 (accessed on 25 April 2024).
Flatbread. Wikipedia 2024.
US food & drug administration (fda) inspection guides. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/iceci/ inspections/ (accessed on 18 November 2019)
Friedman M, Finot PA (1991) Improvement in the nutritional quality of bread. Adv Exp Med Biol 289:415–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-2626-5_30
Friedman M, Gumbmann MR (1987) Effect of sulfur amino acid supplementation of raw soy flour on the growth and pancreatic weights of rats. J Nutr 117:1018–1023
Friedman M, Levin CE (2012a) Nutritional and medicinal aspects of D-amino acids. Amino Acids 42:1553–1582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0915-1
Friedman M, Levin CE (2012b) Nutritional value of D-amino acids, D-peptides, and amino acid derivatives in mice. Methods Mol Biol 794:337–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-331-8_23
Friedman M, Gumbmann MR, Ziderman II (1987) Nutritional value and safety in mice of proteins and their admixtures with carbohydrates and vitamin c after heating. J Nutr 117:508–518. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/117.3.508
Friedman M, Levin CE, Lee S-U, Lee J-S, Ohnisi-Kameyama M, Kozukue N (2008) Analysis by HPLC and LC/MS of pungent piperamides in commercial black, white, green, and red whole and ground peppercorns. J Agric Food Chem 56:3028–3036. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf703711z
Friedman, Mendel; Gumbmann, M.R.; Ziderman, I Nutritional and Toxicological Consequences of Browning during Simulated Crust-Baking. In Protein quality and the effects of processing; Phillips, R.D., Finley, J.W., Eds.; Food science and technology; M. Dekker: New York, 1989 ISBN 978–0–8247–7984–9.
García-García J, Gracián C, Baños A, Guillamón E, Gálvez J, Rodriguez-Nogales A, Fonollá J (2023) Beneficial effects of daily consumption of garlic and onion extract concentrate on infectious respiratory diseases in elderly resident volunteers. Nutrients 15:2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15102308
Dietary Guidelines 2015–2020 | Health.Gov Available online: https://health.gov/our-work/nutrition-physical-activity/dietary-guidelines/previous-dietary-guidelines/2015 (accessed on 25 April 2024).
Imaizumi VM, Laurindo LF, Manzan B, Guiguer EL, Oshiiwa M, Otoboni AMMB, Araujo AC, Tofano RJ, Barbalho SM (2023) Garlic: a systematic review of the effects on cardiovascular diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 63:6797–6819. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2043821
Jiaqi Z, Zihan D, Heung-Sang Wong S, Chen Z, Tsz-Chun Poon E (2024) Acute effects of various doses of nitrate-rich beetroot juice on high-intensity interval exercise responses in women: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 21:2334680. https://doi.org/10.1080/15502783.2024.2334680
Kahlon T, Friedman M (2024) Composition of flatbreads prepared from blue, red, yellow, and white corn flours supplemented with edible ecklonia cava algae. Food Nutr J. https://doi.org/10.29011/2575-7091.100193
Kalinová PJ, Tříska J, Hořejší K (2023) Comparison of the main constituents in two varieties of proso millet using GC–MS. Foods 12:2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122294
Lebwohl B, Ludvigsson JF, Green PHR (2015) Celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMJ 351:h4347. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h4347
Lee SU, Lee JH, Choi SH, Lee JS, Ohnisi-Kameyama M, Kozukue N, Levin CE, Friedman M (2008) Flavonoid content in fresh, home-processed, and light-exposed onions and in dehydrated commercial onion products. J Agric Food Chem 56:8541–8548. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf801009p
Li X, Kahlon T, Wang SC, Friedman M (2021a) low acrylamide flatbreads from colored corn and other flours. Foods 10:2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102495
Li X, Kahlon T, Wang SC, Friedman M (2021b) Low acrylamide flatbreads prepared from colored rice flours and relationship to asparagine and proximate content of flours and flatbreads. Foods 10:2909. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122909
Lozada DN, Pulicherla SR, Holguin FO (2023) Widely targeted metabolomics reveals metabolite diversity in jalapeño and serrano chile peppers (Capsicum Annuum L.). Metabolites 13:288. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020288
Mahalakshmi B, Sivasubramanian N, Vaghela P, Ganvanthbhai RD, Rajeshbhai GP, Ramalakshmi G, Prakash D, Ekambaram G (2022) Effect of beta vulgaris extracts on dysmenorrhea among adolescent girls. Bioinformation 18:657–660. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630018657
Muramatsu D, Uchiyama H, Higashi H, Kida H, Iwai A (2023) Effects of heat degradation of betanin in red beetroot (Beta Vulgaris L.) on biological activity and antioxidant capacity. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286255
Qarooni J, Ponte JG, Posner ES (1992) Flat breads of the world. Cereal Foods World 37:863
Rakita S, Kokić B, Manoni M, Mazzoleni S, Lin P, Luciano A, Ottoboni M, Cheli F, Pinotti L (2023) Cold-pressed oilseed cakes as alternative and sustainable feed ingredients: a review. Foods 12:432. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12030432
Rounds L, Havens CM, Feinstein Y, Friedman M, Ravishankar S (2013) Concentration-dependent inhibition of escherichia coli O157:H7 and heterocyclic amines in heated ground beef patties by apple and olive extracts, onion powder and clove bud oil. Meat Sci 94:461–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.03.010
Scott S, Murray-Kolb L, Wenger M, Udipi S, Ghugre P, Boy E, Haas J (2018) Cognitive performance in Indian school-going adolescents is positively affected by consumption of iron-biofortified pearl millet: a 6-month randomized controlled efficacy trial. J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxy113
Sirotkin AV (2023) Peppers and their constituents against obesity. Biol Futur 74:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-023-00174-3
Sobhana PP, Kandlakunta B, Nagaraju R, Thappatla D, Epparapalli S, Vemula SR, Gavaravarapu SRM, Korrapati D (2020) Human clinical trial to assess the effect of consumption of multigrain indian bread on glycemic regulation in type 2 diabetic participants. J Food Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13465
Soujanya KV, Jayadeep AP (2022) Obesity-associated biochemical markers of inflammation and the role of grain phytochemicals. J Food Biochem 46:e14257. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14257
USDA, 2015. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015–2020 (https://health.gov/our-work/nutrition-physical-activity/dietary-guidelines/previous-dietary-guidelines/2015
Vitale M, Costabile G, Bergia RE, Hjorth T, Campbell WW, Landberg R, Riccardi G, Giacco R (2023) The effects of mediterranean diets with low or high glycemic index on plasma glucose and insulin profiles are different in adult men and women: data from medgi-carb randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr 42:2022–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2023.08.016
Wang H, Shen Q, Fu Y, Liu Z, Wu T, Wang C, Zhao Q (2023) Effects on diabetic mice of consuming lipid extracted from foxtail millet (Setaria Italica): gut microbiota analysis and serum metabolomics. J Agric Food Chem 71:10075–10086. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02179
Water Activity in Foods Safefoods 360. Available online: https://safefood360.com/free- resources/whitepapers/preview/water-activity-in-foods/ (accessed on 18 November 2019).
Zong G, Gao A, Hu FB, Sun Q (2016) Whole grain intake and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Circulation 133:2370–2380. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.021101
Author Information
Healthy Processed Foods Research, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Albany, USA