Morpho-physiological studies and selection criteria in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) under rainfed condition
Singh Vijay Veer, Sharma Hariom Kumar, Sharma Laxman, Rai Pramod Kumar
Research Articles | Published: 23 May, 2024
First Page: 1121
Last Page: 1130
Views: 2512
Keywords: Indian mustard, Drought susceptibility index, Membrane stability index, Relative water content, Correlation, Principal component analysis
Abstract
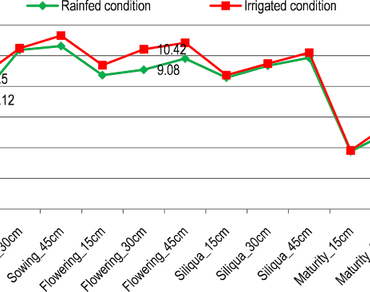
After groundnut and soybean, rapeseed-mustard is the third largest contributor (18.5%) to total domestic availability of edible oil in India. Among rapeseed-mustard, Brassica juncea (Indian mustard L.) is cultivated on more than 80% of total rapeseed-mustard area. Nearly 17% of the total rapeseed-mustard area in India is under rainfed conditions where crop suffers from moisture stress. Therefore, the present investigation was carried out to study the effect of moisture stress on Indian mustard and to identify promising donors for rainfed condition. A total of 100 germplasm accessions of Indian mustard were grown in augmented block design with six checks in two environments (rainfed and irrigated). The rainfed trial received only rainwater as a source of irrigation during the period. While, two irrigations were given to irrigated crop. The data were recorded for eleven traits namely; days to initiation of flowering, days to 50% flowering, days to maturity, 1000-seed weight, seed yield/plant, SPAD chlorophyll, relative water content (RWC), membrane stability index (MSI), excised-leaf water loss, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll stability index. Moisture stress caused maximum reduction in MSI both at the siliqua stage (27.14%) and maturity stage (33.02%) while in morphological traits maximum reduction in seed yield/plant (15.33%) was noticed in comparison to irrigated crop. Four genotypes (DRMR 64, DRMR 67, DRMR 72, DRMR 78) showed high seed yield (> 19.04 g) and 1000-seed weight (5.14 g) under rainfed condition in comparison to best checks (DRMR 150 − 35, RH 406). Genotypes with low drought susceptibility index (DSI) and high stress tolerance index were considered drought tolerant. Eight genotypes (DRMR-75, DRMR-374, DRMR-120, DRMR-139, DRMR-413, DRMR-390, DRMR-405, DRMR-383) were better than the best check RH 406 (DSI = 0.27) in terms of DSI. In conclusion, selection based on more than one parameter including associated agro-morphological traits, physiological parameters, and stress indices helped to identify the genotypes for drought tolerance in Indian mustard.
References
Akanksha, Srivastava K, Srivastava A, Sinha B (2021) Analysis of drought susceptibility index in Indian mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern and Coss]. Ind J Agril Res 55(4):446–451. https://doi.org/10.18805/IJARe.A-5526
Ashraf M, Harris PIC (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynth 51:163–190
Ashraf M, Mehmood S (1990) Response of four brassica species to drought stress. Environ Exp Bot 30(1):93–100
Chauhan JS, Tyagi MK, Kumar A, Nashaat NI, Singh M, Singh NB, Jakhar ML, Welham SJ (2007) Drought effects on yield and its components in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L). Plant Breed 126:399–402
Choudhary RL, Langadi AK, Jat RS, Anupama, Singh HV, Meena MD, Dotaniya ML, Meena MK, Premi OP, Rai PK (2021) Mitigating moisture stress in Indian mustard (B. Juncea) through polymer. J Oilseed Brassica 12(1):21–27
Clarke JM (1987) Use of physiological and morphological traits in breeding programmes to improve drought resistance of cereals. In: Srivastava JP, Porcedo E, Acevedo E, Verma S (eds) Drought tolerance in winter cereals. Wiley, New York, pp 171–190
Dhaliwal SS, Sharma V, Shukla AK, Kaur M, Verma V, Sandhu PS, Alsuhaibani AM, Gaber A, Hossain A (2022) Biofortification of oil quality, yield, and nutrient uptake in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) by foliar application of boron and nitrogen. Front Plant Sci 13:976391. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.976391
Fischer RA, Maurer R (1978) Drought resistance and spring wheat cultivar. l. Grain yield responses. Aust J Agric Res 29:897–912
Govt. of India (2022) Agriculture statistics at a glance 2021, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Department of Economics and Statistics, Government of India, 431 pages
Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica 4(1):9
Jones MM, Turner NC (1978) Osmotic adjustment in leaves of sorghum in response to water deficits. Plant Physiol 61:122–126
Kaur R, Sharma AK, Rani R, Mawlong I, Rai PK (2019) Medicinal qualities of mustard oil and its role in human health against chronic diseases: a review. Asian J Dairy Food Res 38(2):98–104
Koleyoreas SA (1958) A new method for determining drought resistance. Plant Physiol 33:232–233
Kumari A, Avtar R, Narula A, Jattan M, Rani B, Manmohan (2019) Screening for drought tolerance in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes based on yield contributing characters and physiological parameters. J Oilseed Brassica 10(1):1–7
Kumawat BL, Sharma DD, Jat SC (1997) Effect of brassinosteroid on yield and yield attributing characteristics under water deficit stress condition in mustard (B. Juncea L). Ann Biol 13:91–93
Majidi MM, Rashidi F, Sharafi Y (2015) Physiological traits related to drought tolerance in Brassica. Inter J Plant Prod 9:541–560
Morgan JM (1984) Osmoregulation and water stress in higher plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 35:299–319
Mostafaei E, Zehtab-Salmasi S, Salehi-Lisar Y, Ghassemi-Golezani K (2018) Changes in photosynthetic pigments, osmolytes and antioxidants of Indian mustard by drought and exogenous polyamines. Acta Biol Hung 69(3):313–324. https://doi.org/10.1556/018.68.2018.3.7
Naghavi MR, Aboughadareh AP, Khalili M (2013) Evaluation of drought tolerance indices for screening some of corn (Zea mays L.) cultivars under environmental conditions. Not Sci Biol 5(3):388–393
Premachandra GS, Saneoka H, Ogata S (1990) Cell membrane stability an indicator of drought tolerance as affected by applied nitrogen in soybean. J Agril Sci Camb 115:63–66
Rai PK, Sharma HK, Singh VV, Singh KH, Sharma P, Meena HS, Meena BL (2023) Notified rapeseed-mustard varieties in India. Published by ICAR-Directorate of Rapeseed-Mustard Research, Sewar, Bharatpur-321303, Rajasthan, India. ISNB. 978-81-966257-1-9
Ram B, Meena HS, Singh VV, Singh BK, Nanjundan J, Kumar A, Singh SP, Bhogal NS, Singh D (2015) High temperature stress tolerance in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) germplasm as evaluated by membrane stability index and excised-leaf water loss techniques. J Oilseed Brassica 5(2):149–157
Rosielle AA, Hamblin J (1981) Theoretical aspects of selection for yield in stress and non-stress environments. Crop Sci 21:943–946
Salekdeh GH, Reynolds M, Bennett J, Boyer J (2009) Conceptual framework for drought phenotyping during molecular breeding. Trends Plant Sci 14:488–496
Sharma HK, Singh VV, Kumar A, Meena HS, Meena BL, Sharma P, Rai PK (2022) Genetic study of terminal heat stress in indigenous collections of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) germplasm. J Environ Biol 43:161–169
Sharma HK, Kumar A, Singh VV, Meena HS, Priyamedha, Sharma P, Rai PK (2021) Variability and genetic diversity study based on agro-morphological traits in a diverse set of Indian mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. & Coss.] Germplasm. J Environ Biol 42:1495–1504
Shoaf T, Lium BW (1976) Improved extraction of chlorophyll a and b from algae using dimethyll sulfoxide,- Limnal. Oceanog 21:920–928
Singh M, Chauhan JS, Meena SS (2009) Drought induced changes in water use efficiency and other morpho-physiological characters in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) 16th Australian Research Assembly on Brassicas. Ballarat Victoria, Australia, pp 14–16
Singh RP, Singh DP (1988) Plant water relation as selection criteria for drought tolerance in mustard. Biol Plant (Praha) 30(3):231–233
Singh RP, Singh DP, Singh P (1988) Variation for plant water relations and yield structure in Brassica juncea L. under drought conditions. Narendra Deva J Agric Res 3:91–98
Singh SP, Choudhary AK (2003) Selection criteria for drought tolerance in Indian mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern and Coss]. Indian J Genet Pl Breed 63(3):263–264
Singh VV, Garg P, Meena HS, Meena ML (2018) Drought stress response of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.) genotypes. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 7(3):2519–2526. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.703.291
Singh VV, Ram B, Singh M, Meena ML, Chauhan JS (2014) Generation mean analysis of water stress tolerance parameters in Indian mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern & Coss] crosses. SABRAO J Breed Genet 46(1):76–80
Solanki RS, Kumar P, Mishra SP, Ramgiry SR (2017) Contribution of agro-morphologic traits in seed yield of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern & Coss) germplasm under rainfed condition. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6(9):2281–2286. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.609.279
SPSS (2007) SPSS Inc, released. SPSS for Windows, Version 16.0. SPSS Inc, Chicago
Author Information
ICAR-Directorate of Rapeseed-Mustard Research, Bharatpur, India