Comparative study of antifungal potential of various extracts of leaves of Carissa carandas Linn., Nerium oleander Linn. and Allamanda cathartica Linn. against human fungal pathogen Candida albicans
Research Articles | Published: 27 October, 2023
First Page: 1847
Last Page: 1854
Views: 3328
Keywords: Antifungal activity, Crude extracts and secondary metabolites, Disc diffusion assay, Minimum inhibitory concentration, Total activity
Abstract
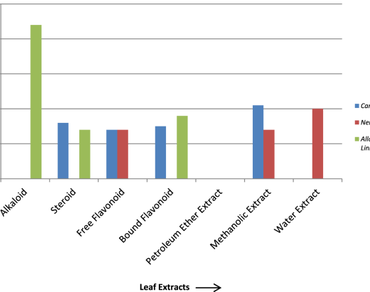
Candida albicans is the most significant species of opportunistic fungus that causes infections in immunocompromised people with invasive fungal illnesses. Scientists are now paying more attention to herbs used in traditional medicine as a result of Candida species’ resistance to antifungal medications. This study was conducted to compare the antifungal impacts of herbal leaf extracts of Carissa carandas Linn., Nerium oleander Linn., and Allamanda cathartica Linn. due to the limitations in the treatment of fungal diseases, like high prices, adverse side effects, drug resistance, or reduced susceptibility to fungal drugs. Leaves were collected, dried, and extracted using standard techniques for alkaloids, flavonoids, steroids, and crude extracts in petroleum ether, methanol, and water, then tested for their antifungal efficacy. A disc diffusion assay was used for screening, and the inhibition zone and activity index were calculated. The broth micro dilution method was used to calculate the minimum inhibitory concentration and the minimum fungicidal concentration. Total activity, mean, and standard deviation were also calculated. Alkaloid extracts of A. cathartica Linn. showed the best activity (IZ = 22 mm, AI = 0.650.01, MIC = 0.078, MFC = 0.156 mg/mL, TA = 557.69 mL). Results showed that among all the examined leaf extracts from the three selected plants, the alkaloid extract of A. cathartica Linn. leaves was the most efficient against Candida albicans. As a result, this plant may be investigated for the development of novel and improved herbal antifungal medications.
References
Andrews JM (2001) BSAC standardized disc susceptibility testing method. J Antimicrob Chemother 4:43–57
Bameta A, Kumari A, Upadhyaya A (2017) Phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activity of Nerium oleander Linn. Phytochem Anal 2:2455–6548
Basri DF, Fan SH (2005) The potential of aqueous and acetone extracts of gall of Quercusinfectoria as antibacterial agents. Indian J Pharmacol 37:26–29
Bongomin F, Gago S, Oladele RO, Denning DW (2017) Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases-estimate precision. J Fungus 3(4):57
Brain KR, Turner TD (1975) The practical evaluation of phytopharmaceuticals. Wright-Scientica, Bristol, pp 57–58
Chaudhary K, Prasad DN (2018) Antimicrobial studies on Nerium oleander Linn. leaves (White Kaner leaves). Int Res J Pharm 9(2):45–47
Dardona AWY, Shahabuddin D (2022) Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of methanolic and ethanolic extracts of three varieties of Nerium oleander. J Pharm Negat 13(7):1821–1829
Demain AL, Sanchez S (2009) Microbial drug discovery: 80 years of progress. J Antibiot 62:5–16
Devanaboyina N, RamaLakshmi N, Satyanarayana B, Sudeepthi P, Hemachakradhar K, Pavankumar RN (2013) Preliminary phytochemical screening, quantitative estimation and evaluation of antimicrobial activity of Alstoniamacrophylla stem bark. Int J Sci Invent Today 2(1):31–39
Dhatwalia J, Kumari A, Verma R et al (2021) Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and nutraceutical profile of carissa species: an updated review. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227010
Eloff JN (2004) Quantifying the bioactivity of the plant extracts during screening and bioassay-guided fractionation. Phytomedicine 11(4):370–371
Evans WC (1996) ‘Trease & Evans’ pharmacognosy, 14th edn. WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, p 573
Fartyal M (2016a) Allamanda cathartica Linn.: extraction and pharmaceutical evaluation of various extracts of leaves and flowers. Int J Curr Pharm Res 8(4):28–32. https://doi.org/10.22159/ijcpr.2016v8i4.15272
Fartyal M (2016b) Antifungal sscreening of alkaloids, flavonoids & steroids of different parts of Nerium oleander Linn. Int J Acad Res 3,7(4):132–141
Fartyal M, Kumar P (2014a) Bioactivity of crude extracts of Carissa carandas Linn. Linn. Linn. extracted in polar and non-polar solvents. Int J Eng SciInnov Technol 3(5):186
Fartyal M, Kumar P (2014b) Bioactivity of crude extracts of Nerium oleander Linn. extracted in polar and non-polar solvents. J Sci Innov Res 3(4):426–432
Fartyal M, Kumar P (2016a) Antifungal efficacy of alkaloids, flavonoids and steroids of different parts of Carissa carandas Linn. Linn. Linn. Asian J Sci Technol 7(8):3353–3357
Fartyal M, Kumar P (2016b) Pharmacological evaluation of crude extracts of Allamanda cathartica linn. extracted in polar and non-polar solvents. Int J Curr Res 8(8):35730–35735
Gong Y, Liu W, Huang X, Hao L, Li Y, Sun S (2019) Antifungal activity and potential mechanism of N-butylphthalide alone and in combination with fluconazole against Candida albicans. Front Microbiol 10:1461. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01461
Harborne JB (1973) Phytochemical methods. Chapman & Hall, Ltd., London, pp 49–188
Hema K, Krishnaveni R (2014) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of Allamanda cathartica Linn. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 5:588–593
Jia Z, Tang M, Wu J (1999) The determination of flavonoid content in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem 64(4):555–599
Massiha A, Muradov PZ (2015) Comparison of antifungal activity of extracts of ten plant species and griseofulvin against human pathogenic dermatophytes. Zahedan J Res Med Sci 17(10):e2096
Mehta R, Dhruv S, Kaushik V, Sen KK, Khan NS, Abhishek A, Dixit AK, Tripathi VN (2020) A comparative study of antibacterial and antifungal activities of extracts from four indigenous plants. Bioinformation 16(3):267–273. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630016267
Nath MC, Chakravorty MK, Chowdhury SR (1946) Liebermann-Burchard reaction for steroids. Natur 157(3978):103–104
Petricevich VL, Abarca-Vargas R (2019) Allamanda cathartica: a review of the phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, and biotechnology. Molecules 24:1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071238
Pilasombut K, Laosinwattana C, Tuyen Nguyen TK, Ngamyeeesoon N, Teerarak M (2019) Antimicrobial properties of extracts from Carissa carandas Linn. Linn. L. fruits and its application in chilled and frozen ground pork. Int J AgricTechnol 15(1):91–102
Ramawat KG, Merillon JM (2000) Biotechnology: secondary metabolites. Science Pub Inc.
Scio E, Mendes RF, Motta EVS, Bellozi PMQ (2012) Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of some plant extract. Phytochemicals as Nutraceuticals-Global Approaches to their Role in Nutrition and Health, INTECH Europe, pp 21–42
Singh S, Bajpai M, Mishra P (2020) Carissa carandas Linn. Linn. L.—Phyto-pharmacological review. J Pharm Pharmacol 72:1694–1714
Sofowara A (1993) Medicinal plants & traditional medicine in Africa. Spectrum Books Ltd, Ibadan, p 289
Subramanian SS, Nagarjan S (1969) Flavonoids of the seeds of Crotolariaretusa and Crotolariastriata. Curr Sci 38:65
Suleyman G, Alangaden GJ (2016) Nosocomial fungal infections: epidemiology, infection control, and prevention. Infect Dis Clin North Am 30:1023–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2010.11.003
Supaphon P, Preedanon S (2019) Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of endophytic fungi extracts isolated from Carissa carandas Linn. Linn. Afr J Microbiol Res 13(27):464–473
Talapko J, Juzbašić M, Matijević T, PustijanacE BS, Kotris I, Škrlec I (2021) Candida albicans—the virulence factors and clinical manifestations of infection. J Fungus 7(2):79
Tomita Y, Uomori A, Minato H (1970) Steroidal sapogenins and sterols in tissue cultures of Dioscoreatokora. Phytochemistry 9:111–114
Verma S, Chaudhary HS (2011) Effect of Carissa carandas against clinically pathogenic bacterial strains. J Pharm Res 4:3769–3771
Wankhede SB, Routh MM, Rajput SB, Karuppayil SM (2013) Antifungal properties of selected plants of Apocynaceae family against the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Int Curr Pharm J 2(7):122–125
Author Information
Department of Biotechnology, Kanoria PG Mahila Mahavidhyalaya, Jaipur, India