Analyses of virulence and genetic diversity among Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Vignicola isolates from different cowpea varieties
Olatunde Bukola Ibiyemi, Afolabi Olakunle Bamikole, Oguntade Oluwole, Onasanya Amos Adeyinka, Okiki Pius Abimbola
Research Articles | Published: 15 January, 2024
First Page: 476
Last Page: 485
Views: 3212
Keywords: Xanthomonas axonopodis , Cluster analysis, Morphotype c, Genotype, PCR polymorphism
Abstract
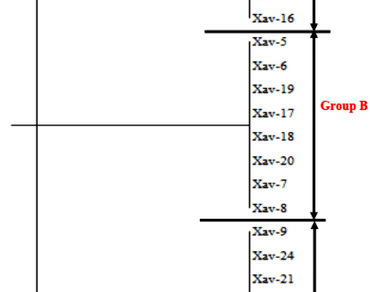
Xanthomonas is a genus of proteobacteria that causes plant diseases and affects many crops around the world, including tree crops, leaf and fruit vegetables, cereals, tubers, and other crops. The goal of this study was to conduct comparative analyses of morphological, genetic, and virulence factors, as well as to determine the genotype distribution of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vignicola (Xav). To determine the cultural morphology, twenty-four (24) pure cultures of Xav from four (4) cowpea varieties were obtained from the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) in Ibadan, Nigeria and cultured on nutrient agar with 5% glucose. The isolates’ genomic DNA was extracted and randomly amplified using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers to obtain polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products, which were electrophoresed on 2% and 1.4% agarose gel for purification and polymorphism determination. However, cultural morphology revealed that Xav has a distinctive yellow color with varying intensities. Among the 24 Xav isolates, cluster analysis revealed three (3) morphologies, two (2) major genotypes, and two (2) major virulence genes (16SrRNA and cylA). The correlation between morphology, virulence, and genotype revealed that color intensity is strongly related to genotype as well as pathogenicity of the isolates. As a result of this study’s findings, it is possible to conclude that all of the isolates have pathogenic effects, albeit at varying levels of expression.
References
Abiodun O, Adetunji O, Pius O, Folusho O, Tolulope O, Amos O, Oyewale M (2019) Virulence characteristics and phylogenetic background of antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus faecalis from abattoir, poultry and clinical origin in Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria. Afr J Microbiol Res 13(30):700–709
Adhikari TB, Basnyat RC, Mew TW (1999) Virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae Pv. Oryzae on rice lines containing single resistance genes and gene combinations. Plant Dis 83(1):46–50
Amos O, Ekperigin MM, Afolabi A, Onasanya RO, Ojo AA, Ingelbrecht I (2013) Two genotypes of Xanthomonas oryzae Pv Oryzae virulence identified in West Africa. Int J Genet Mol Biol 5(3):28–36
Basso A, Onasanya A, Issaka S, Sido AY, Haougui A, Adam T, Sere Y, Saadou M (2011) The brown rot of rice in Niger: pathological diversity of isolates collected from the irrigated areas. J Appl BioSci 38:2551–2563
Büttner D, Bonas U (2010) Regulation and secretion of Xanthomonas virulence factors. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34(2):107–133
Chala A, Kebede T, Blomme G (2016) Natural occurrence and pathogenicity of Xanthomonas bacteria on selected plants. Afr J Biotechnol 15(39):2146–2155
Donahoo RS, Jones JB, Lacy GH, Stromberg VK, Norman DJ (2013) Genetic analyses of Xanthomonas axonopodis Pv. Dieffenbachiae strains reveal distinct phylogenetic groups. Phytopathology 103(3):237–244
Dordas C (2008) Role of nutrients in controlling plant diseases in sustainable agriculture. A review. Agron Sust Dev 28(1):33–46
Duche TR, Omoigui L, Iheukwumere CC (2015) Variations among Xanthomonas axonopodis Pv. Vignicola isolates in Benue State, Nigeria. Intl J Innov Sci Res 13(1):271–278
Ellis SD, Boehm MJ, Coplin D (2008) Bacterial diseases of plants. 6th Fact sheet Agriculture and Natural Resources, The Ohio State University. PP401
Gena M, Shah R, Jadon KS, Mali BL (2009) Host range of Xanthomonas axonopodis Pv. Vignicola, the incitant of bacterial blight in cowpea. Indian Phytopathol 62(4):539–540
Jacques MA, Arlat M, Boulanger A, Boureau T, Carrère S, Cesbron S, Chen NW, Cociancich S, Darrasse A, Denancé N, Le Fischer M (2016) Using ecology, physiology, and genomics to understand host specificity in Xanthomonas. Annual Rev Phytopathol 54:163–187
Mahuku GS, Jara C, Henriquez MA, Castellanos G, Cuasquer J (2006) Genotypic characterization of the Common Bean bacterial blight pathogens, Xanthomonas axonopodis Pv. Phaseoli and Xanthomonas axonopodis Pv. Phaseoli var. Fuscans by rep-PCR and PCR–RFLP of the ribosomal genes. J Phytopathol 154(1):35–44
Nelson RJ, Baraoidan MR, Cruz CM, Yap IV, Leach JE, Mew TW, Leung H (1994) Relationship between phylogeny and pathotype for the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(9):3275–3283
Olawale AK, Salako RJ, Olawale AO, Famurewa O (2015) Antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus faecalis isolated from food canteens in Osun States, Nigeria. Br Microbiol Res J 6(4):196–206
Onasanya A, Ekperigin MM, Nwilene FE, Sere Y, Onasanya RO (2009) Two pathotypes of Xanthomonas oryzae Pv. Oryzae. Curr Res Bacteriol 2(2):22–35
Onasanya A, Ekperigin MM, Onasanya RO, Obafemi TO, Ogundipe AT, Ojo AA, Ingelbrecht I (2018) DNA sequencing analysis of African Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae virulence gene (Axavrg) DNA marker. Sci Agric Bohem 49(2):78–86
Onasanya A, Mignouna HD, Thottappilly G (2003) Genetic fingerprinting and phylogenetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Nigeria. Afr J Biotechnol 2(8):246–250
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc: Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system version 2.2. Exeter Publications, Setauket, NY
Sedgley C, Nagel A, Dahlén G, Reit C, Molander A (2006) Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and culture analyses of Enterococcus faecalis in root canals. J Endodont 32(3):173–177
Sere Y, Onasanya A, Verdier V, Akator K, Ouedraogo LS, Segda Z, Mbare MM, Sido AY, Basso A (2005) Rice bacterial leaf blight in West Africa: preliminary studies on disease in farmers’ fields and screening released varieties for resistance to the bacteria. Asian J Plant Sci 4(6):577–579
Sneath PH, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy. The principles and practice of numerical classification
Sunde PT, Olsen I, Debelian GJ, Tronstad L (2002) Microbiota of periapical lesions refractory to endodontic therapy. J Endodont 28(4):304–310
Swofford DL (1990) Phylogeny reconstruction. Mol Syst 411–501
Author Information
Molecular Biology Unit, Department of Biological Sciences, College of Sciences, Afe Babalola University, Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria