Acute and sub-chronic toxicity studies of aqueous and ethanol extracts of Triumfetta rhomboidea (Tiliaceae) Leaf in healthy albino rats
Research Articles | Published: 27 October, 2023
First Page: 2532
Last Page: 2541
Views: 3311
Keywords: Cholesterol, Histopathology, Liver function, Oxidative stress, n Triumfetta rhomboidean
Abstract
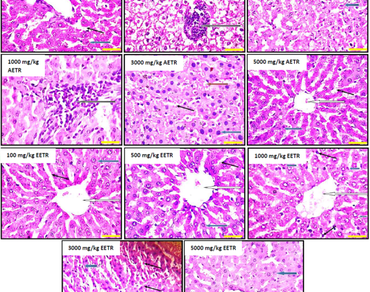
Medicinal plants contain chemical substances that can modulate biological processes similar to synthetic drugs and also demonstrate certain degree of toxicity. The current study investigated the safety of aqueous and ethanol extracts of Triumfetta rhomboidea leaves in normal male albino rats. Leaves of T. rhomboidea were collected and prepared to obtain aqueous (AETR) and ethanol (EETR) extracts of T. rhomboidea. Acute toxicity testing followed standard procedure. In sub-chronic testing, animals were allotted into 6 groups containing 5 animals each: Animals in group 1 (control) were given distilled water while groups 2–6 were respectively administered 100, 500, 1000, 3000 and 5000 mg extract/kg body weight daily in single dose using oral gavage. After 28th days of extracts dosing, rats were sacrificed and samples were collected for biochemical analysis. The results of LD50 revealed toxicity level above 5000 mg extract/kg for AETR and EETR in acute exposure. Sub-chronic administration of AETR and EETR caused significant (P < 0.05) increase in rat body weight. Doses of AETR and EETR demonstrated significant reduction in AST, ALP, GGT, creatinine while only high doses above 3000 mg AETR/kg significantly (P < 0.05) elevated urea. Despite cholesterol was significantly elevated in AETR and EETR treated animals, the concentration of HDL-C also increased significantly. Conclusively, this study has experimentally demonstrated the safety of aqueous and ethanol extracts of Triumfetta rhomboidea, but caution should be observed when extrapolating these results in humans because continuous dosing could alter organ structures.
References
Akindele AJ, Oladimeji-Salami JA, Oyetola RA, Osiagwu DD (2018) Sub-chronic toxicity of the Hydroethanolic Leaf Extract of Telfairia occidentalis Hook. f. (Cucurbitaceae) in male rats. Medicines 5:4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5010004
Akintimehin E, Onoagbe I, Abu O (2022) Proximate composition, qualitative phytochemicals screening and In-vitro antioxidant potential of Triumfetta rhomboidea leaves extracts. Trends in Sciences 19(24):3033. https://doi.org/10.48048/tis.2022.3033
Akintimehin ES, Karigidi KO, Omogunwa TS, Adetuyi FO (2021) Safety assessment of oral administration of ethanol extract of Justicia carnea leaf in healthy wistar rats: hematology, antioxidative and histology studies. Clin Phytosci 7:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-020-00234-4
Akpovona AE, Onoagbe IO, Eze GI, Omonkhua AA (2016) Acute and sub-chronic toxicity studies of ethanol extract of terminalia macroptera stem bark in wistar albino rats. JMBR: a peer-review. J Biomed Sci 15(1):62–73
Alkali YI, Jimoh AO, Muhammad U (2018) Acute and sub-chronic toxicity studies of methanol Leaf Extract of Cassia singueana F. (Fresen) in Wistar rats. Herb Med 4(2):6
Arsad SS, Mohd EN, Hamzah H, Othman F (2013) Evaluation of acute, subacute and subchronic oral toxicity of Rhaphidophora decursiva (Roxb.) Schott extract in male Sprague Dawley rats. J Med Plant res 7:3030–3040
Avwioro OG (2010) Histochemistry and tissue pathology, principle and techniques. Claverianum press, Ibadan, Nigeria
Bosch CH (2011) Triumfetta rhomboidea Jacq. [Internet] Record from PROTA4U. Brink, M. & Achigan-Dako, E.G. (Editors). PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa /Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen, Netherlands. http://www.prota4u.org/search.asp
Chung-Hung C, Gek-Cheng N, Yusoff R (2012) A brief review on antidiabetic plants: global distribution, active ingredients, extraction techniques and acting mechanisms. Pharmacogn Rev 6(11):22–28
Han LK, Zheng YN, Xu BJ, Okuda H, Kimura Y (2002) Saponins from platycodi radix ameliorate high fat diet induced obesity in mice. J Nutri 132(8):2241–2245
Hounkpatin HO, Fraser SDS, Glidewell L, Blakeman T, Lewington A, Roderick PJ (2019) Predicting Risk of recurrent Acute kidney Injury: a systematic review. Nephron 142(2):83–90
Jones HB, Nugent D, Jenkins R (2010) Variation in characteristics of islets of Langerhans in insulin-resistant, diabetic and non-diabetic-rat strains. Int J Exp Path 91:288–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00713.x
Kifayatullah M, Mustafa MS, Sengupta P et al (2015) Evaluation of the acute and sub-acute toxicity of the ethanolic extract of Pericampylus glaucus (Lam.) Merr. In BALB/c mice. J Acute Disease 4(4):309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2015.06.010
Longnecker D (2014) Anatomy and histology of the pancreas. Exocrine Pancreas Knowledge Base, Pancreapedia. https://doi.org/10.3998/panc.2014.3
Lorke D (1983) A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Archive of Toxicology 53:275–289
Mahomoodally MF (2013) Traditional medicines in Africa: An appraisal of ten potent African medicinal plants. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013; 2013:617459
Mounanga MB, Mewonob L, Angone SA (2015) Toxicity studies of medicinal plants used in sub-saharan Africa. J Ethnopharmacol 174:618–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.005
Muhammad S, Hassan LG, Dangoggo SM, Hassan SW, Umar KJ, Aliyu RU (2011) Acute and subchronic toxicity studies of kernel extract of Sclerocarya birrea in rats. Sci World J 6(3):11–14
National Research Council (1997) Occupational Health and Safety in the Care and Use of Research animals. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/4988
Neuwinger HD (2000) African traditional medicine: a dictionary of plant use and applications. Medpharm Scientific, Stuttgart, Germany. 589 pp
Olaniyan JM, Muhammad HL, Makun HA, Busari MB, Abdullah AS (2016) Acute and sub-acute toxicity studies of aqueous and methanol extracts of Nelsonia Campestris in rats. J Acute Disease 5(1):62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2015.08.006
Oso BJ, Oyewo EB, Oladiji AT (2019) Influence of ethanolic extracts of dried fruit of Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich on haematological and biochemical parameters in healthy Wistar rats. Clin Phytosci 5:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-019-0104-4
Roberts S, James RC, Franklin MR (2003) Hepatotoxicity: toxic effects on the liver. In: Williams PL, James RC, Roberts SM (eds) Principles of toxicology: environmental and industrial applications, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, pp 111–128
Suresh R, Tomy S, Ujwala TK, Celine S, Padma VM (2015) Antidiabetic activity of petroleum ether extract of triumfetta rhomboidea on streptozotocin induced diabetic rat model. World J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci 4(10):822–828
Wang X, Zhang W, Wang Y, Peng D et al (2010) Acute and sub-chronic oral toxicological evaluations of quinocetone in Wistar rats. Reg Toxic Pharmacol 58:421–427
Author Information
Biochemistry Unit, Department of Chemical Sciences, School of Sciences, Olusegun Agagu University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Nigeria